Biodiversity・Ecosystem conservation
What is biodiversity?
Global warming is affecting the life of many creatures on earth.
A wide variety of living creatures inhabit earth and each fulfills an important role in sustaining the life of others.
For example, plants produce oxygen enabling humans and animals to live. Bees carry pollen which allows crops to bear fruit.
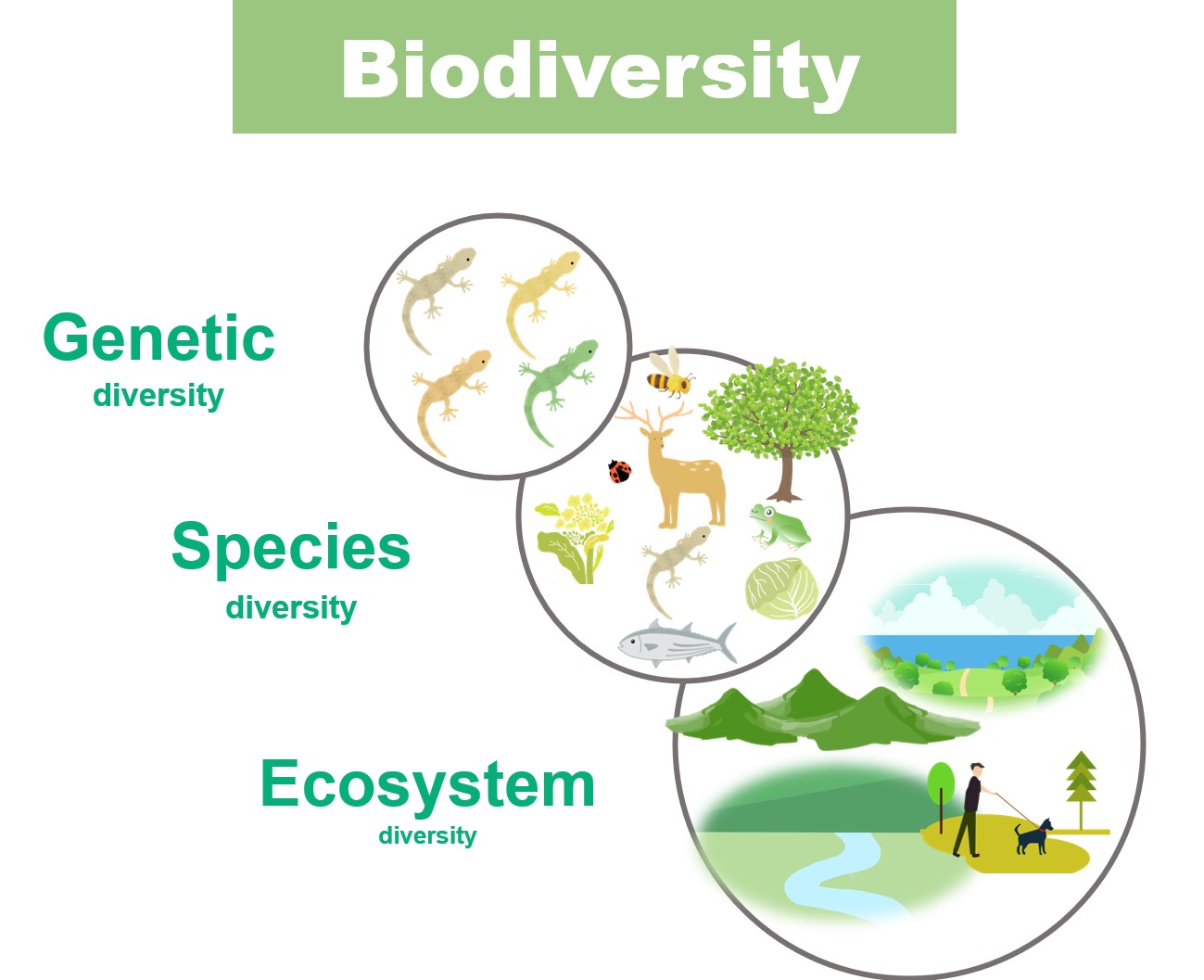
Biodiversity refers to the rich variety of life on earth which is interacting with each other. There are three levels of biodiversity: genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity.
From the video ‘Global environmental issues and the Anthropocene‘.
Biodiversity loss
Currently, we are losing the species biodiversity at a very fast rate. More than 44,000 species are already extinct or threatened with extinction.
More than 44,000 species
are
threatened with extinction

Source:IUCN (2024)
The rate at which species are going extinct far exceeds the rate of naturally occurring extinctions.
It is currently happening at the fastest rate in millions of years and is therefore often called the sixth major extinction period in Earth’s history.
Organisms extinct since 1500

Source:IPBES (2020)
The main causes include overhunting and poaching, habitat loss due to deforestation and land development, global warming, invasive species, and water and air pollution.
Causes of biodiversity loss
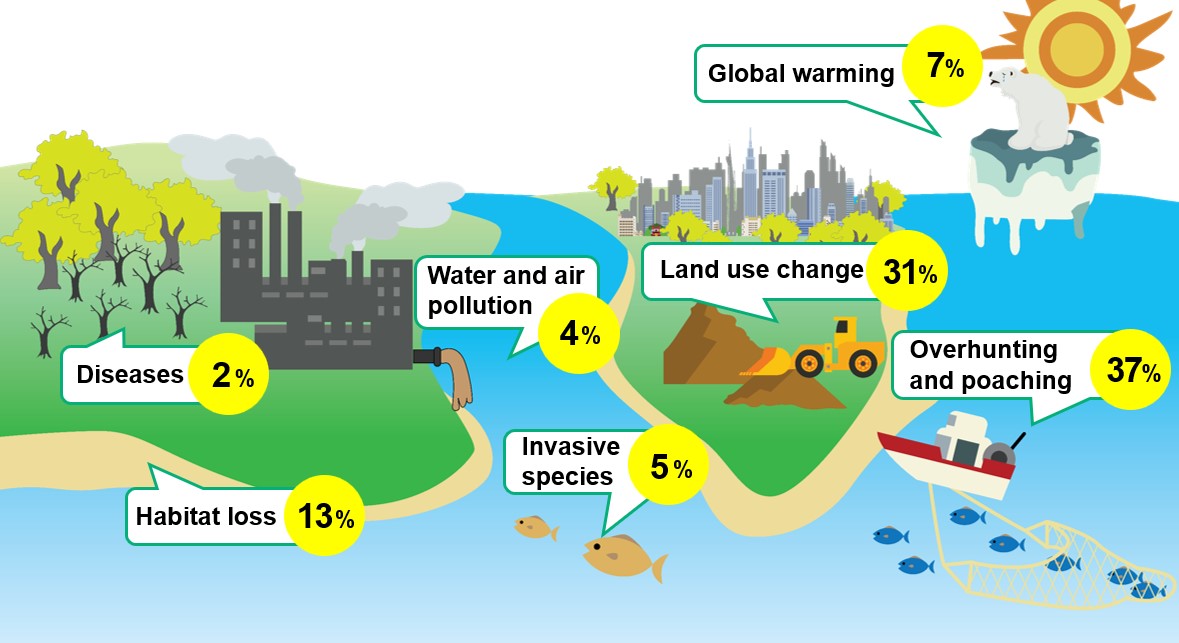

From the video ‘Global environmental issues and the Anthropocene‘.
Source:Monastersky (2014)
Blessings of nature (Ecosystem services)
The biological (plants, animals, etc.) and non-biological (light, temperature, etc.) environments are collectively referred to as ecosystems.
Humans benefit from ecosystems in various ways, such as silk and cotton for clothing, wood to construct buildings, and plants to make medicines.Thesebenefits we receive from ecosystemsare called ecosystem services.
When biodiversity declines, ecosystem services also decline, which in turn will have a significant impact on our life.
Ecosystems are connected with each other through land, air, and oceans. Human society is also connected through international transportation of goods and services. Therefore, even if the loss of species is happening in distant from where the majority of humans are living, the effects may spread to various parts of the world.
(Written by: Yuko Onishi)
References
Monastersky, R., 2014, Biodiversity: Life – a status report, Nature, 516(7530): 158-161, DOI: 10.1038/516158a.
IPBES, 2019, Summary for policymakers of the global assessment report on biodiversity and ecosystem services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, Díaz, S. et al. (eds.), IPBES secretariat, Bonn, Germany, 56 pages, DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.3553579.(Figure in text refers to Japanese translation by the Ministry of the Environment, IGES)
International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN), 2022, The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, Version 2022-2.
https://www.iucnredlist.org
Video




